venous thromboembolism
what is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)?
A venous thromboembolism is a blood clot that happens in the vein.
why is this a priority to us?
- Clots that form in veins can lead to increased hospitalization, and prolonged medication treatment
- Most significantly, clots can travel through the blood stream and become lodged in other organs such as the lungs, and rarely the brain leading to very significant medical complications
who’s at risk?
- Pre-teens and teens have risk factors similar to adults. Being overweight, inactive, smoking, using certain medications such as birth control, and certain medical conditions put patients at risk for developing clots
- In kids, having central lines, such as a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line is a significant risk factor for developing clots
what are we doing to reduce clots?
- We actively screen our patients for risk factors
- For patients at risk, we encourage walking, use devices that squeeze the calves, or sometimes use medications to reduce the risk of clots
- We are engaged in the work with Solutions for Patient Safety trying to understand why children develop clots with IVs and what the best steps are to prevent them. By sharing with other hospitals in the network, we can accelerate our learning and find solutions faster
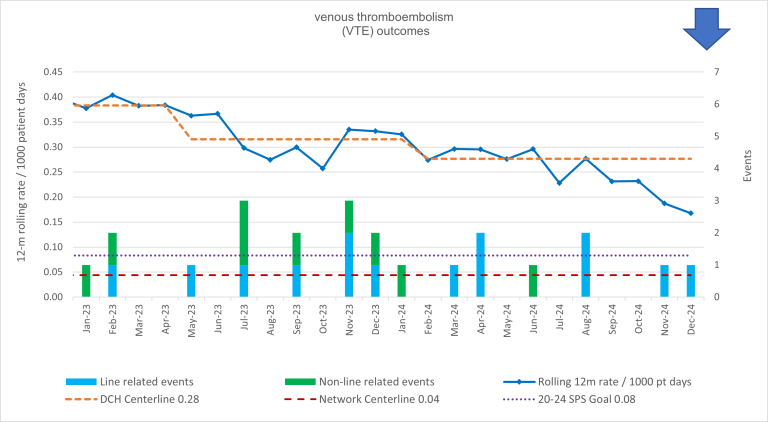
what do we measure?
- We measure the number of clots per 1000 patient days